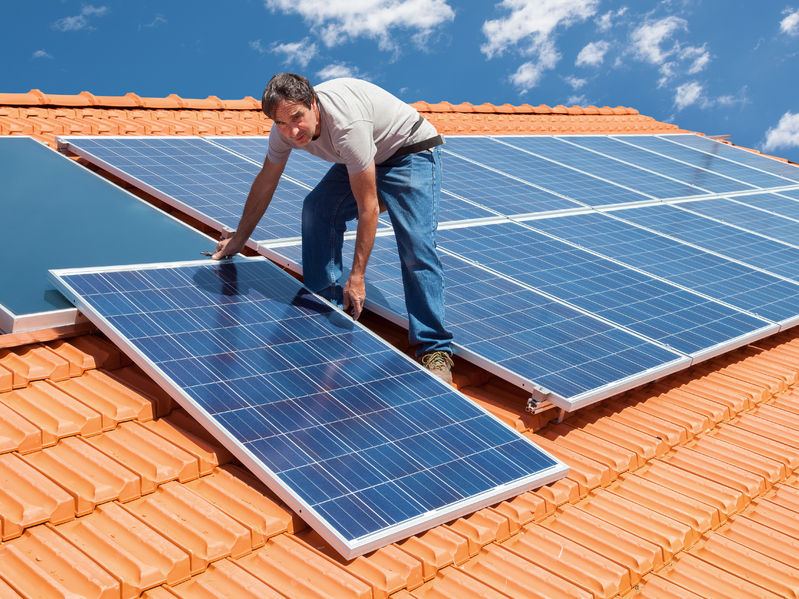
What are photovoltaic cells, or solar cells?
A unique material (semiconductor) is used to construct a PV cell. Electricity is produced solely by absorbing photon energy. The material releases electrons if it receives enough sunlight. The purpose of the cell’s front is to collect these stray electrons. The electrons travel to the front of the cell as a result of this.
History of Solar Energy
The image of a solar cell glistering in the sun illustrates many magazine articles on modern technology. But the means of converting light energy into electrical energy is nothing new. A.E. Becquerel made the first observation of the photovoltaic effect in 1839, which occurs when light strikes an electrode dipped in an electrolyte and generates a current. American scientist Charles Frits created the first solar cell in 1984, which allowed for the exploitation of this phenomenon. Frits used the less-than-economic design of semi-conductive selenium coated in a thin layer of gold to achieve the conversation at an efficiency of just 1%. The cell works by absorbing energy in the form of photons of light, which then displace electrons in the semiconductor, generating a current. Due to the lower efficiency, no one was ever going to power their home with these cells.
Solar technology benefited from the introduction of silicon semiconductors in 1941. Developments in the 1950s and 1960s increased the efficiency of domestic applications and became a light-weight power source for spacecraft and satellites. Researchers have been working hard to mop up this energy by using certain devices, and one of them is a solar cell, or photovoltaic cell. Three scientists named Calvin Fubber, Gerald Pearson, and Daryl Chapin made the breakthrough in 1954 at Bell Laboratories. And they created the first solar cell made of high-quality solar cells for everyday use. Material scientists have identified potential III-V semiconductor compounds, nanotechnology, and organic materials that can be used in the design and development of solar cells, also known as photovoltaic (PV) cells. It is important to point out that PV cells are not only environmentally friendly, but they also offer clean, efficient, reliable, and uninterrupted sources of electrical energy.
The amount of energy from the sun’s radiation falling on just 1 square kilometer is about 4000 megawatts more than enough to light a big city. The technology is still inefficient today, with commercial cells performing at only ground 13% and the world record standing at 4.28%. Still, this is enough to power homes, Outdoor gadgets and spacecraft.
Technology and basic principles behind solar cell
At the point when light sparkles on a photovoltaic (PV) cell, it might be reflected, consumed, or go directly through it. The PV cell is made out of semiconductor material, which joins a few properties of metals and a few properties of separators. That makes it exceptionally equipped for changing over light into power. At the point when light is consumed by a semiconductor, photons of light can exchange their vitality to electrons, enabling the electrons to move through the material as electrical current. This present streams out of the semiconductor to metal contacts and after that advances out to control your home and whatever is left of the electric matrix. There are a wide range of semiconductor materials utilized as a part of sun oriented cells.
According to studies, 55% of modern solar cells are made of polycrystalline silicon innovation, 30% of them of single gem silicon innovation, 5.6 percent of undefined silicon (a-Si), 6 percent of a-Si-on-CZ cut, and 3.5 percent by thin-film and less than 1% cells made of organic cells and concentrated cells. There are various sun-based cells electrically associated with each other and mounted in a help structure or casing is known as a photovoltaic module. Modules are intended to supply power at a specific voltage, for example, a typical 12 volts framework. The current generated is specifically dependent on how much light strikes the module. When multiple modules are wired together, it’s called array and the larger the area of array, the more electricity can be produced.