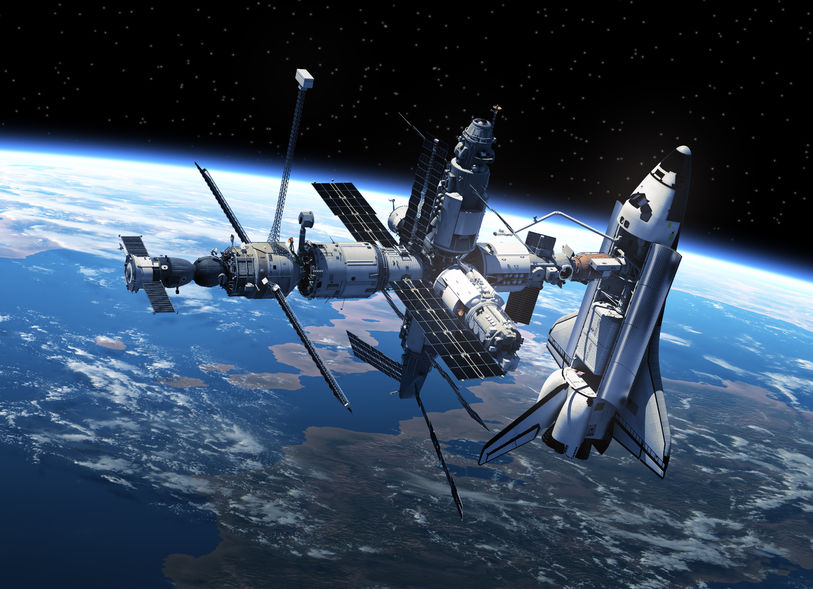
The International Space Station (ISS) is the most talked-about subject. What is it? Most people want to know what it really means. The International Space Station is basically an artificial satellite, or, you can say, a large spacecraft. It is a place where the astronauts live. So, if you wonder where the astronauts live, then the mystery has been sorted out because they have a home up there.
Do you know that it is also a science lab? The ISS serves as a microgravity and is mainly used for it’s research laboratories, ranging from biology, human biology, physics, astronomy, meteorology, and other fields. The universe is so big, and there are multiple concepts to study. What if the astronauts find a peculiar meteorite or an unfamiliar object? They would go back to the science lab and study it.
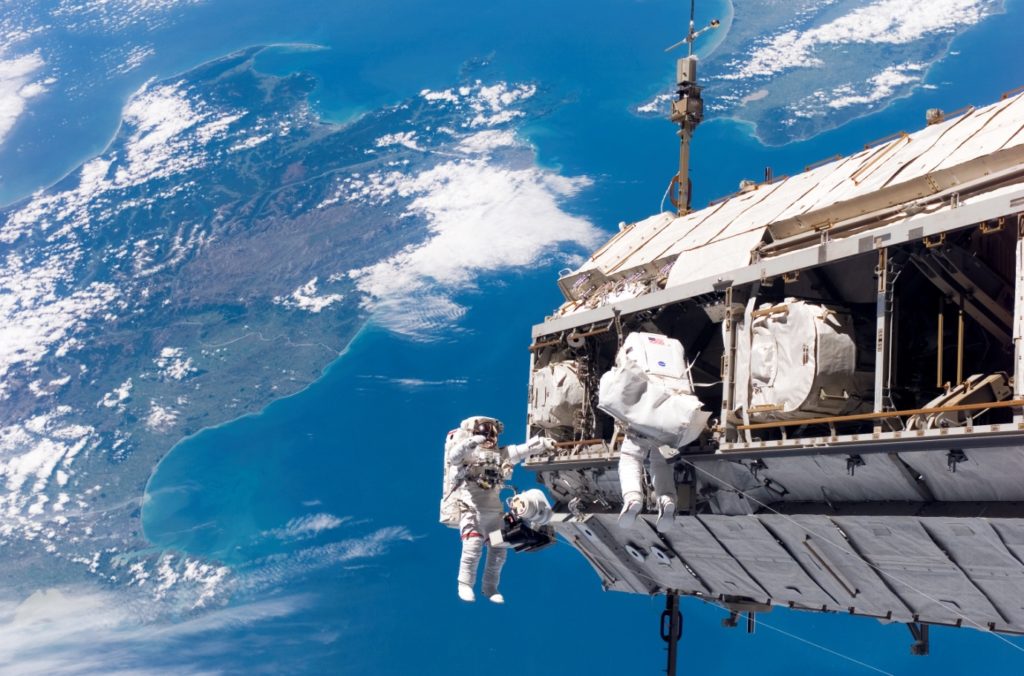

Who has built it?
There are many countries behind the International Space Station. They built it together for the astronauts. There are no discriminations up in the sky as they work together under the same space station. The astronauts used a variety of pieces to construct the space station. NASA uses this space station to learn more about space and working or living in space.
The first piece was launched in the year 1998, and it took two years to build the entire space station. It was in the year 2000 when the first crew landed on the space station. Many more pieces were added later on, and whenever astronauts visit the space station, they stay on the International Space Station. The parts of the space station are called modules. The modules are called nodes, and they connect the parts of the station from one to another.
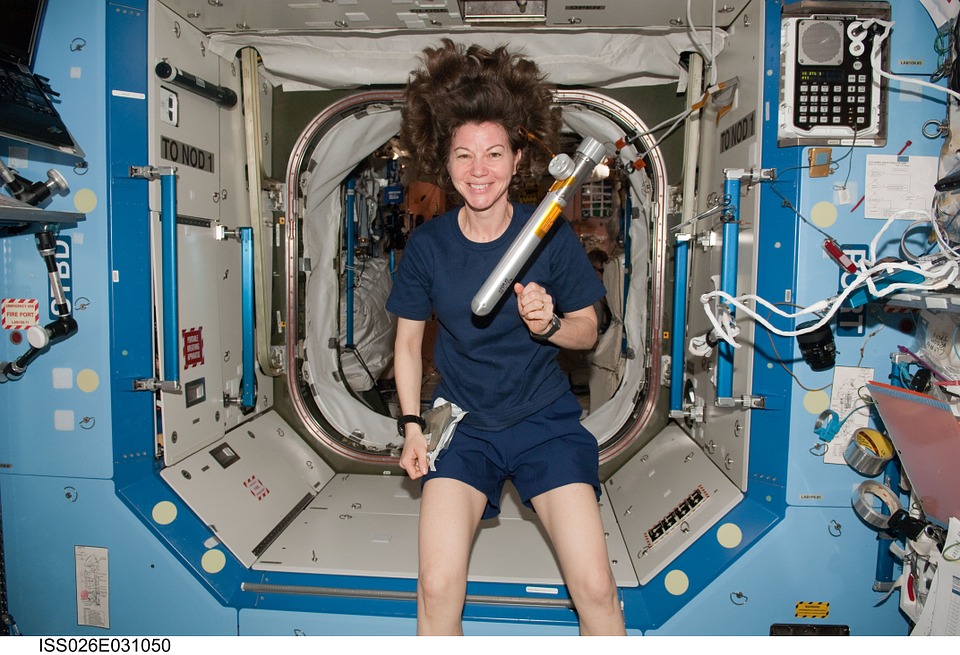

How big is the space station?
The space station has five bedrooms. It is a home for the astronauts. The house contains two bathrooms as well as a gymnasium. You can get a good workout up in space as well. Six astronauts can live inside the house, and it is built for their comfort and convenience. It is a big station and weighs more than a million pounds.
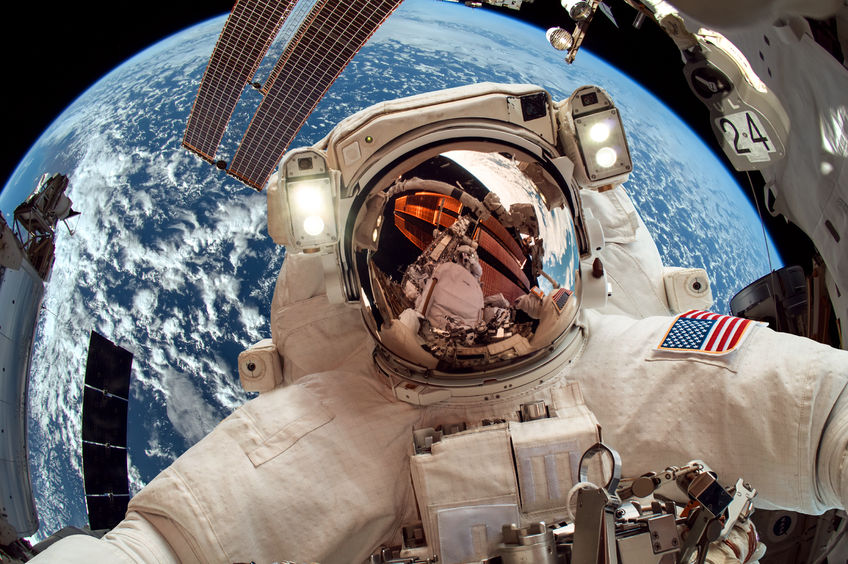

How do they get electricity?
There are solar arrays on the space station that collect energy from the sun. The energy from the sun is converted into electricity. There are robot arms outside, which helped in building the International Space Station.
Just imagine that there is a home out there that includes five bedrooms and electricity. Astronauts stay there and workout. We have seen pictures of astronauts playing guitar and having a fun time up there. There is a home on the orbit. Some research work cannot be done on Earth, so the space station is the ideal place for carrying out the research.
Water is dangerous to use on the space station because it could cause choking if the astronauts inhale it. They use wet/moist wipes up there. Sunita Williams had to chop off her long hair before the mission because personal hygiene became a problem up there. As for health conditions, the face bloats up and the stomach feels funny. Everything tastes like cardboard on a space station because smell and taste senses are diminished in space. You will not get the taste of dishes that you get on Earth.
NASA has major plans to send humans into deep space, and this is just one way to start. Scientists are able to study the living conditions in space. Since astronauts are living in space, they can find out what it is like. What are the challenges that they face? The structure of the space station is like an interconnecting tube. It has wing-like panels as well. It looks like a satellite, but it is actually a home for the astronauts. It takes two days to reach the space station, but the experience is extraordinary. To think that a home is built in orbit is plausible. Would NASA send us to a space station as well? We just have to wait and watch!
Summary
The ISS orbits Earth around 240 miles above its surface, traveling at a remarkable 17,500 miles per hour. However, it is more than simply a fast spaceship; it is a cutting-edge science laboratory where astronauts and cosmonauts live and work.
Here are some critical details about the ISS:
Construction and collaboration:
The United States and Russia were primarily responsible for building the International Space Station in low-earth orbit. It included contributions from international cooperation.
It was originally known as “Freedom” in the 1980s before being redesigned to reduce costs and increase international participation. In 1993, the United States and Russia integrated their respective space station plans, which included modules from the European Space Agency (ESA) and Japan.
Assembly Timeline:
In November 1998, the Russian control module Zarya launched, and the United States’ Unity linking node did the same the following month.
Scientists gradually added more modules, laboratories, and solar panels to form a complex structure conducive to scientific inquiry.
Living and Research:
The International Space Station houses astronauts and cosmonauts on a rotating basis. They carry out studies, test technologies, and investigate the effects of space on biology and human health.
Neuro-degenerative illnesses, space botany, microgravity-induced fluid changes, and algae-based life support systems are among the research areas.
Visiting vehicles:
Various nations use reusable spacecraft to send resupply flights to the International Space Station. These include: ESA, JAXA, Roscosmos, Northrop Grumman, SpaceX, and Boeing.
Crew spacecraft from NASA, Roscosmos, SpaceX, and Boeing also ferry astronauts to and from the station.