The atmosphere affects the sun’s color, so during the morning, evening, and afternoon, the sun appears reddish, yellow, or white. This happens because our earth’s atmosphere scatters light. Red light has the highest wavelength, so during the morning only red light reaches our eyes, and all the other colors of the visible spectrum get scattered away.
All other colors have smaller wavelengths than red light, and during the morning and evening, the sun is at the farthest distance from the earth’s surface, which makes scattering possible.

The Sun is actually a 4.5 billion-year-old star that is made up of hydrogen and helium. It is actually 150 million kilometers away from Earth.
1.3 million earths can fit in the sun; this shows how big our sun is.
The sun’s gravity is so strong that it holds our solar system (all planets) together.
The sun is the only source of life on earth. Without the sun, nothing can survive on earth. Even plants make their food using sunlight. Without the sun, everything on earth will freeze in the cold and die.
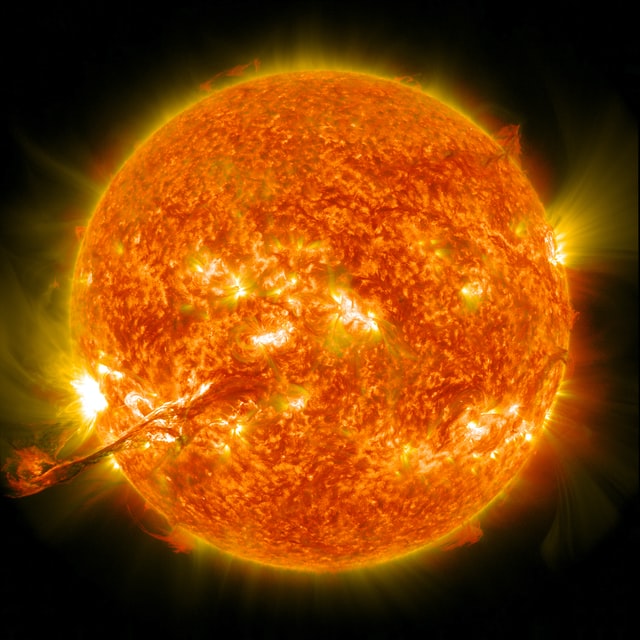
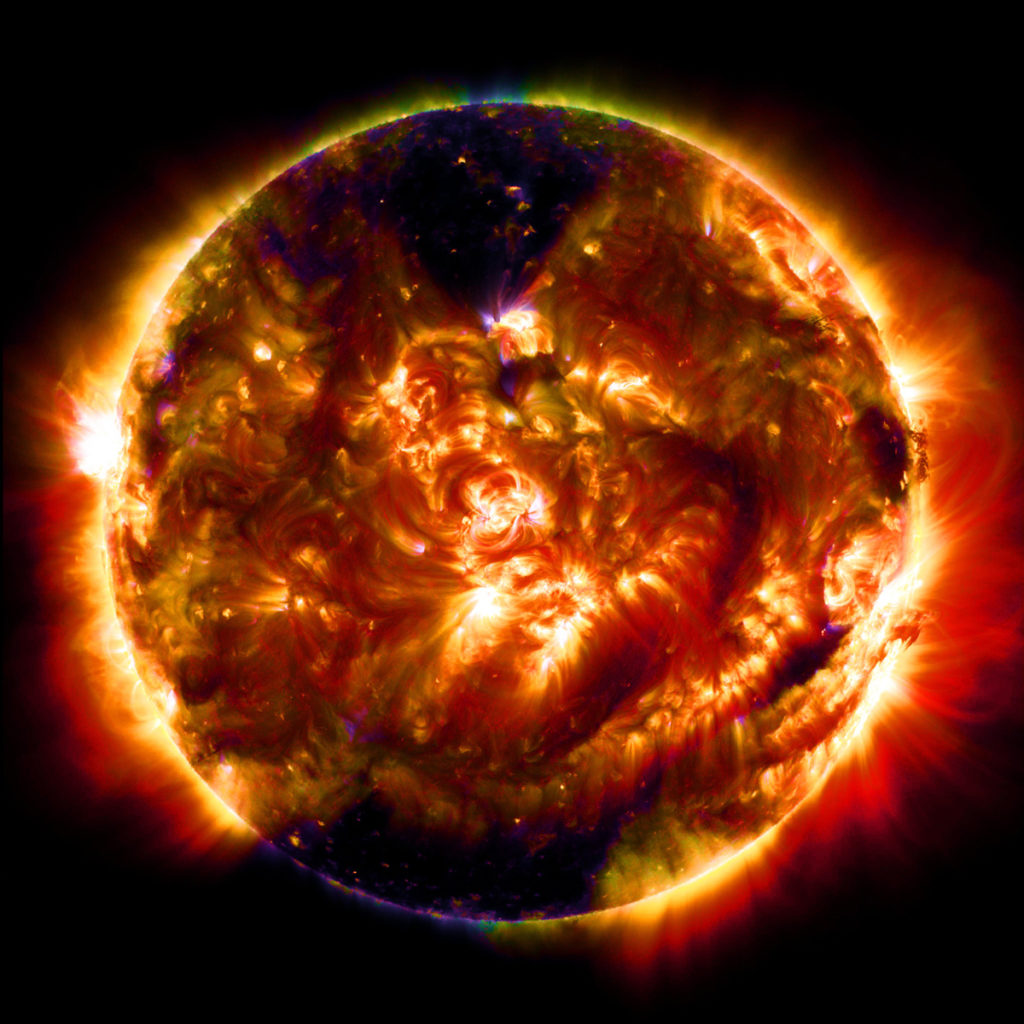
The surface temperature of the sun is 5,500 degrees Celsius, which is more than enough to boil diamonds and graphite.
It takes 8 minutes for sunlight to reach the earth’s surface, so if someday the sun disappears, we can only notice this after 8 minutes.
The sun is not yellow or red in color, but it is actually white in color, and we notice yellow and red due to the earth’s atmosphere, which causes scattering of light just like a prism, so when you see the sun as red, it means only the red light of the sun is coming to your eyes and the rest of the colors are getting scattered after hitting the air. The sun’s actual color is white, not red or yellow, and the white color is made up of all the visible colors.
1,000 Jupiter-sized planets can fit inside the sun.

Some Amazing Facts
Size of the Sun:
The Sun is the largest thing in our solar system.
It’s about 695,508 kilometers from its center to its surface.
The Sun holds 99.86% of the entire solar system’s mass.
Imagine it like this: it could fit around 1.3 million Earths inside!
Sun as a Star:
The Sun is an average-sized star.
Some stars are tiny (just a tenth of the Sun’s size), while others are over 700 times bigger.
Because of its massive weight and strong gravity, the Sun is almost a perfect sphere.
Sun’s Hot Core:
The core of the Sun is the hottest part.
It sizzles at a scorching 15 million degrees Celsius!
Here, hydrogen atoms join together to form helium atoms in a process called thermonuclear fusion.
This releases an incredible amount of energy in the form of heat and light.
Temperature Journey:
The energy created in the core takes a million years to reach the outer layer (called the convective zone).
There, the temperature drops to around two million degrees Celsius.
By the time it reaches the surface, it’s a cooler 5,973°C—still hot enough to boil diamonds!
Mystery of the Corona:
Above the surface, in the Sun’s atmosphere (called the corona), the temperature rises again to roughly two million degrees Celsius.
Oddly, as we move farther from the core, we’d expect the temperature to drop. But this dramatic increase in the atmosphere remains one of the Sun’s biggest secrets!
What Is the Sun Made Of?
The Sun is like a big ball of gas and plasma.
About 91% of it is hydrogen gas.
When it gets super hot and feels the squeeze from gravity, this hydrogen fuses into helium during a process called nuclear fusion.
Solar Wind and Auroras:
When the plasma on the Sun gets really toasty, it’s packed with energy.
Charged particles can escape the Sun’s gravity and zoom out into space. We call this speedy escape the solar wind.
Sometimes, when this solar wind hits Earth’s atmosphere, it creates beautiful light shows like the Northern Lights (auroras).
Other Elements in the Sun:
Besides hydrogen and helium, scientists have found 65 other elements in the Sun.
Some of the most common ones include oxygen, carbon, nitrogen, silicon, magnesium, neon, iron, and sulfur.
Sun’s Rotation:
Even though the sun isn’t as solid as the earth, it still spins.
On average, it takes 27 Earth days for the Sun to do one full rotation.
Different parts of the Sun move at different speeds: the equator takes 24 days, while the polar regions take over 30 days.
Cool Spots Called Sunspots:
Sunspots are like cooler patches on the Sun’s surface.
They hang out in the photosphere (that’s the Sun’s outer layer).
To us, they look darker than the warmer plasma around them.
These spots can be huge, up to 50,000 kilometers across!
They are believed to be the result of strong magnetic fields interfering with the sun’s core radiation, which cools things down.

References:
https://www.nhm.ac.uk/discover/factfile-the-sun.html